

However, the risk is low unless the patient has a genetic predisposition to this, or uses nicotine. DVT or PEĪny lower limb injury, and / or surgery performed, carries a risk of DVT (clotting in the leg veins). However, in most cases this will respond to strengthening work. Although they can run, they describe the power as reduced. Some patients notice some weakness following the surgery. It is possible that the pain may be from another source if the pain is not relieved with the surgery. If a "window" or section of the fascia is excised, rather than dividing it, there may be a reduced risk of recurrence. However this is rarely a significant problem, and it only involves the skin, and does not affect any muscles.
#COMPARTMENTS OF LEG FASCIOTOMY SKIN#
There may be an area of numbness distal to on of the incision, where the skin nerves are cut to gain access to the fascia. The risk is higher when smaller incisions are used. A collection of blood, hematoma or "pseudo aneurysm" may form and this would may have to be removed during a return to theatre, but this is rare. Veins may be damaged during the surgical exposure, but this causes bruises only and these resolve with time. These can usually be treated with a course of antibiotics, but some may need to have the wound If the non-operative measures fail and the patient wants to return to, or continue running, surgical release of the compartments is indicated. The goal of the surgery is to reduce the pressure within the compartments of the leg which is achieved by dividing the lining of each compartment so that it can expand and thus reduce the pressure and allow sufficient blood flow during exercise.ĭespite the best sterile techniques, there is a low risk of wound infections (1%) and even lower risk of deep infection (fraction of 1%). Other sources of leg pain should be excluded. If the pressures are significantly increased this confirms the diagnosis. This test involves measuring the pressures within each compartment of the leg, before and after exercise has been performed to the point that symptoms are present. Porter may require compartment pressure studies to be performed.
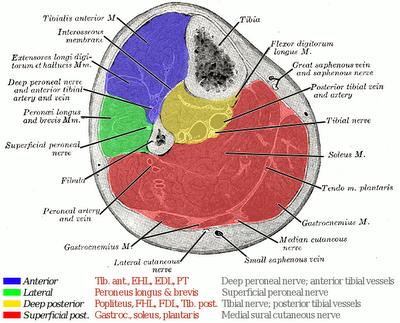
The diagnosis may be based on clinical features alone, or Dr. However, all compartments of the leg require treatment in most cases. The pain may be localised to one of the compartments of the leg, often the anterior or front compartment, however it can effect some or all of the leg compartments. A heel-striking foot-slapping type running style is associated with the condition and should be corrected with gait analysis and gait re-training. The non-operative treatment includes stretching work, myofascial releases and other physiotherapy treatments. This causes oxygen deprivation and hence pain.

The cause of the problem is that the compartments in which the muscles are located, are too tight, and when the blood flow increases to the exercising muscles, the pressure increases to the point that blood can no longer flow into the muscle. Some patients give up running and the problem goes away. Other activities, including cycling and swimming are pain free. The pain settles completely with rest, but comes back the next time they try running. Once they stop running the pain resolves over a variable period of 20-30 minutes or more. It is usually a tight, cramp like pain, that builds up to the point that running is no longer possible. Usually they can start a run pain free, but after a number of minutes or even kilometers, the pain starts to build up. Patients with CECS commonly present with bilateral running-related leg pain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
